Syslog is a standard for collecting, routing, and storing log messages. It emerged from the Sendmail project in the 1980s. In 2001, it was standardized as RFC 3164 and then as RFC 5424 in 2009. It’s supported on several different platforms, including Unix/Linux, BSD Unix, macOS, and network devices like printers and routers. Because of the remote syslog capability, the standard has lasted several decades.
The ability to route log messages over a network connection has been part of the syslog protocol from the beginning. Instead of being limited to logging messages to a local file, you can direct syslog messages to a logging server.
In this post, you’re going to learn how to redirect syslog messages to Papertrail. You’ll learn about three common syslog daemons, how to redirect them, and how to test your configuration. Then, we’ll wrap up by discussing the advantages of consolidating logs in a centralized system like SolarWinds® Papertrail™.
Remote Syslog Daemons
Which Syslog Daemon?
Depending on which operating system and version your system is running, there are three different syslog daemons. Before you can configure remote syslog, you need to determine which one your system is running.
Syslogd
Syslogd (also sysklogd) is a syslog daemon dating back to the 1980s. You’ll usually see it on BSD Unix, older versions of CentOS and other Linux distributions, and macOS.
Depending on how old the version on your system is, it may not support redirecting logs to a different service port. It also only supports the UDP protocol for sending and receiving log messages, which isn’t always the best option. You may want to consider updating to rsyslog or syslog-ng.
Syslog-ng
Syslog-ng is a newer implementation of the syslog protocol. It adds several new features to logging, such as content-based routing and filtering, a flexible configuration model, and the TCP protocol for transport.
RSyslog
Rsyslog also implements the basic syslog protocol with extensions for content-based filtering and routing. The official website bills it as “the rocket-fast system for log processing.”
Identify Your Syslog Daemon
All syslog daemons store their configurations in the /etc directory. Searching there for files or directories will tell you which one you’re running.
List any files or directories in /etc with syslog in the name.
ls /etc/*syslog*Depending on how your distribution configures syslog, you’ll find a configuration file, directory, or combination of both. The names will match the daemon your system is running.
Here’s a list on an Ubuntu Linux system running rsyslog:
egoebelbecker@hala:~$ ls /etc/*syslog*
/etc/rsyslog.conf
/etc/rsyslog.d:
20-ufw.conf 50-default.conf postfix.conf
Here’s a listing on a CentOS system running syslog-ng:
[egoebelbecker@ops ~]$ ls /etc/*syslog*
/etc/syslog-ng:
conf.d patterndb.d scl.conf syslog-ng.conf
Here’s another system that was running rsyslog but has been switched to syslog-ng:
[egoebelbecker@server1 ~]$ ls /etc/*syslog*
/etc/rsyslog.conf /etc/syslog-hosts
/etc/rsyslog.d:
listen.conf
/etc/syslog-ng:
conf.d patterndb.d scl.conf syslog-ng.conf
There are still configuration files for both daemons there. See which process is running with the ps command.
[egoebelbecker@ops2.sec1 ~]$ ps -ef |grep syslog
root 7258 1 0 2020 ? 00:01:20 /usr/sbin/syslog-ng -F -p /var/run/syslogd.pid
egoebel+ 16674 16629 0 18:50 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto syslog
In the above example, there’s a syslog-ng daemon running.
If ls /etc/syslog doesn’t return anything, you need to install a syslog daemon.
For CentOS, Fedora, or another Red Hat Linux derivative, you can install rsyslog with yum or dnf.
$ sudo yum install rsyslogFor Ubuntu, Mint, or another Debian derivative, use apt.
$ sudo apt install rsyslogFor macOS, use the homebrew package manager. You’ll have to install it on your system if you haven’t already.
$ brew install rsyslogConfigure Remote Syslog
To redirect messages to Papertrail, you need to know your Papertrail server hostname and port. You can get them from the Papertrail web interface at “Add Systems” or “Log Destinations.”
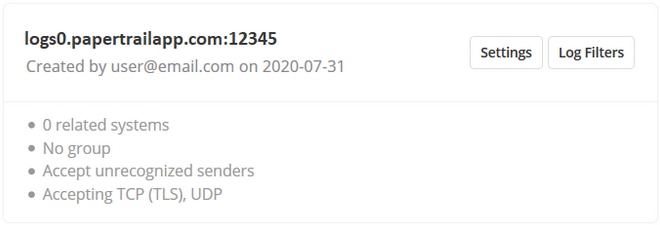
The host and port information on the Papertrail Log Destinationsscreen.
All the syslog daemon configuration files belong to the root user, so you’ll need to either su to the root account or use sudo to edit the files.
Configure Rsyslog
Edit /etc/rsyslog.conf. Add this to the end of the file:
*.* @loghostname.papertrailapp.com:XXXXXWhere loghostname is the prefix of your Papertrail instance and XXXXX is the port number.
Configure Syslogd
The configuration change for syslogd is similar to the one for rsyslog.
Edit /etc/syslog.conf. Add this to the end of the file:
*.* @loghostname.papertrailapp.com:XXXXXWhere loghostname is the prefix of your Papertrail instance and XXXXX is the port number.
Configure Syslog-ng
Edit /etc/syslog-ng.conf or, if that file doesn’t exist, /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf.
First, create a logging destination for Papertrail. Add this block to the configuration file.
destination d_papertrail {
udp("logsN.papertrailapp.com" port(XXXXX));
};
Where loghostname is the prefix of your Papertrail instance and XXXXX is the port number.
Next, find lines starting with source.
For example, this file has several sources.
source s_startctllog { unix-stream("/server/logs/apps-logs/.startctllog.sock" perm(0777) owner("apps") group("apps") max-connections(200)); };
source s_startctludp { udp(ip(0.0.0.0) port(2714) so_rcvbuf(16777216)); };
source s_startctltcp { tcp(ip(0.0.0.0) port(2714) so_rcvbuf(16777216)); };
At the end of the file, paste configuration entries that point your sources at the new Papertrail destination.
log { source(s_startctllog); destination(d_papertrail); };
log { source(s_startctludp); destination(d_papertrail); };
log { source(s_startctltcp); destination(d_papertrail); };
Test Remote Syslog
Testing With Logger
You can test your remote syslog with the logger test tool. It sends log messages to your local syslog daemon.
If logger isn’t installed on your Linux system, most distributions bundle it in a package named bsd-utils or utils-linux. Use the package manager to install it.
You can generate a test message by passing it to logger on the command line.
$ logger "Testing Papertrail message delivery"The test message should appear in the Papertrail event viewer right away.
Troubleshooting
If the message doesn’t arrive, you can verify Papertrail is listening for connections with telnet.
Run telnet with the hostname and port you used in your remote syslog configuration. Instead of separating them with a colon, use a space. You should see something like the following:
$ telnet loghostname.papertrailapp.com XXXXX
Trying XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX...
Connected to loghostname.papertrailapp.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
Exit with Ctrl + ] (right bracket). If telnet can’t connect, check the hostname and port in “Add Systems” or “Log Destinations.”If they match, check your firewall and make sure hosts are allowed to connect to Papertrail.
You can also check the syslog daemon logs. Most log to /var/log in a filename named syslog or syslog-ng.
Taking Advantage of Remote Syslog
Consolidating your log messages into Papertrail provides you with many important benefits and capabilities.
Your logs are indexed and available in a central search interface. Instead of comparing log files side by side in terminal windows or text editors, you can search and view consolidated results on a single page.
Papertrail indexes your logs in real time, so you can view multiple streams on a single page. You can use your logs to trigger events and alerts. Papertrail supports alerting over several channels, including Slack, Pushover, and PagerDuty.
With your logs forwarded to Papertrail, they’re archived in a single location too, saving you the work of figuring out how to collect the logs from multiple hosts and back them up.
Remote Syslog Configuration
In this post, we covered how to determine which syslog daemon your system is running and how to install one if you don’t have one or wish to switch to a more recent version. Then we showed you how to remote syslog with rsyslog, syslog-ng, and syslogd, so you can forward log messages to Papertrail. Finally, we wrapped with how integrating remote syslog with SolarWinds Papertrail can help you with monitoring your applications and infrastructure.
Start improving your monitoring capabilities with Papertrail centralized logging today.
This post was written by Eric Goebelbecker. Eric has worked in the financial markets in New York City for 25 years, developing infrastructure for market data and financial information exchange (FIX) protocol networks. He loves to talk about what makes teams effective (or not so effective!).
Exploring further? You should check out the SolarWinds syslog management tool